Revolutionizing Business Operations: How Advanced Process Management Drives Efficiency and Innovation
?
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are continually seeking ways to enhance their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition. Advanced process management has emerged as a crucial strategy in achieving these goals. By refining and optimizing workflows, businesses can not only streamline their operations but also foster innovation, driving growth and success in an increasingly complex environment.
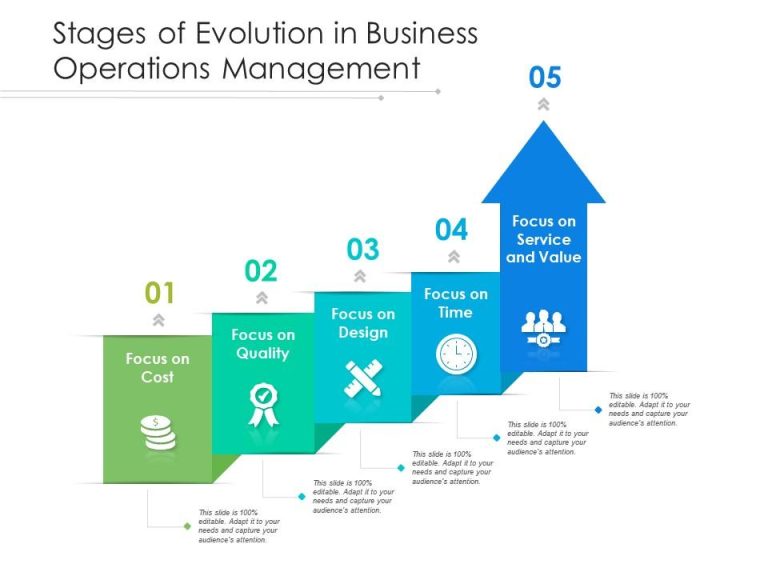
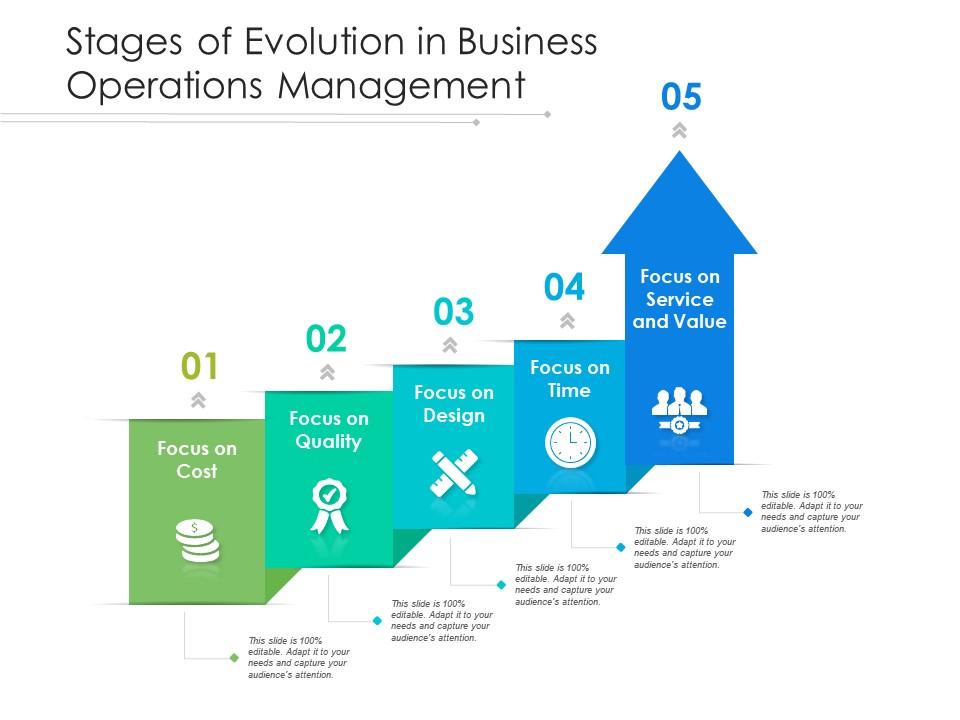
The Evolution of Process Management
Process management has come a long way from its traditional roots. Historically, businesses focused on basic workflow processes to ensure tasks were completed efficiently. However, as technology has advanced and market demands have shifted, the need for a more sophisticated approach has become apparent. Advanced process management incorporates modern tools and methodologies to analyze, design, implement, and continually improve processes.

Data-Driven Decision Making in Modern Management Consultancy

Revolutionizing Business Operations: How Advanced Process Management Drives Efficiency and Innovation

Building Organizational Resilience: Strategies for Management Success | PDCA Group

Adapting to Change: Resilience Strategies for Government Entities

ISO 9001: More Than a Certificate, It’s a Cultural Transformation

Key Components of Advanced Process Management
Data-Driven Insights: Modern process management relies heavily on data analytics. By leveraging real-time data, organizations can gain valuable insights into their operations, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions. Tools such as Business Process Management Systems (BPMS) and advanced analytics platforms allow for continuous monitoring and optimization of processes.
Automation and Technology Integration: Automation is a game-changer in process management. By integrating technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), businesses can automate repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and free up valuable resources. This not only speeds up operations but also allows employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
Agile Methodologies: The adoption of agile methodologies has transformed process management by promoting flexibility and responsiveness. Agile practices, such as iterative development and continuous feedback, enable organizations to adapt quickly to changes and continuously improve their processes.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Advanced process management emphasizes the importance of collaboration across different departments and functions. By breaking down silos and fostering a culture of teamwork, businesses can ensure that processes are integrated and optimized across the entire organization.
Driving Efficiency Through Process Management
Efficiency is a primary goal of process management. By mapping out workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and streamlining procedures, organizations can significantly reduce operational costs and time. Advanced process management techniques, such as Lean Six Sigma, focus on eliminating waste and improving quality, leading to more efficient and effective operations.
Fostering Innovation
In addition to driving efficiency, advanced process management also plays a crucial role in fostering innovation. By creating a structured framework for process improvement, businesses can experiment with new ideas, test innovative solutions, and implement changes more effectively. The iterative nature of advanced process management encourages a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, allowing organizations to stay ahead of industry trends and emerging technologies.
Real-World Examples
Several companies have successfully leveraged advanced process management to revolutionize their operations. For instance, a global manufacturing firm implemented a comprehensive process management system that integrated AI and automation, resulting in a significant reduction in production time and costs. Similarly, a leading financial services provider adopted agile methodologies to streamline its processes, leading to faster time-to-market for new products and improved customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Advanced process management is more than just a trend; it is a fundamental approach to transforming business operations. By embracing data-driven insights, automation, agile practices, and cross-functional collaboration, organizations can enhance efficiency, drive innovation, and achieve long-term success. As businesses continue to navigate an ever-changing landscape, advanced process management will remain a key driver of operational excellence and competitive advantage.
In an era where efficiency and innovation are paramount, investing in advanced process management is not just a strategic choice—it is a necessity for thriving in the modern business world.


